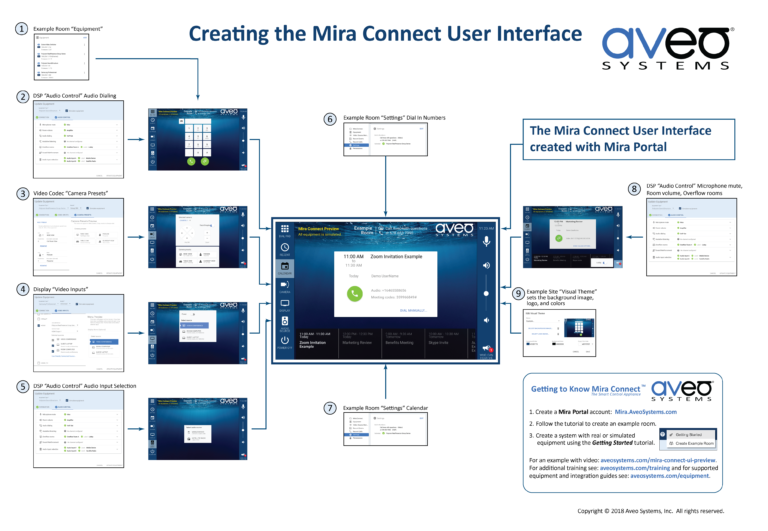
In today’s digital age, user experience (UX) has become a critical factor for businesses, websites, and apps. Understanding the user experience basics is essential for designers, developers, marketers, and business owners who want to create products that delight users and drive engagement.
This comprehensive guide explores the user experience basics, including its definition, core principles, key elements, practical examples, real-world applications, and best practices for improving UX in digital products.
What Are User Experience Basics?
The term user experience refers to the overall experience a person has when interacting with a product, system, or service.
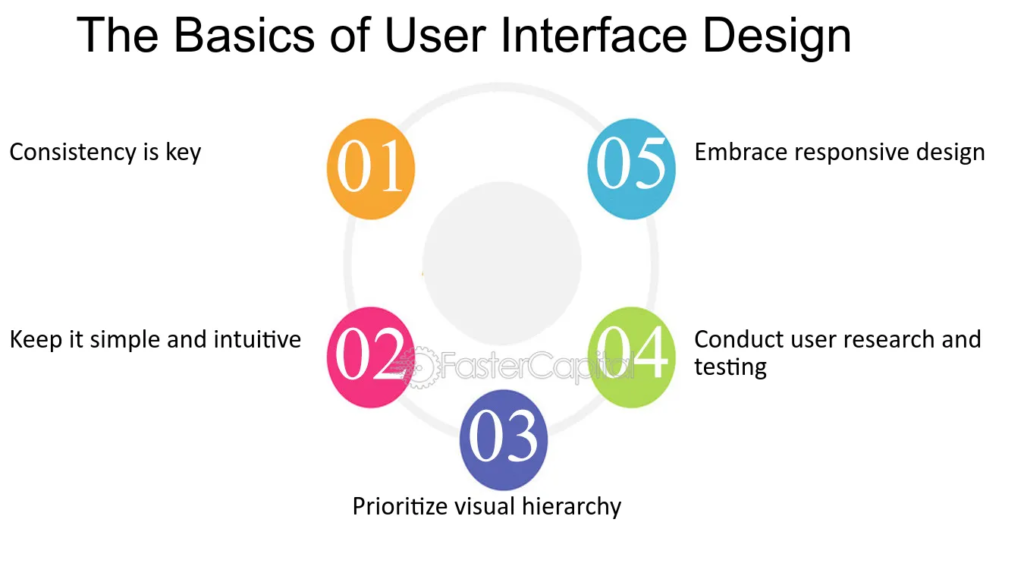
Definition
User experience basics involve understanding how users perceive, feel, and interact with your digital product or service.
User experience is not just about design—it encompasses usability, accessibility, performance, and emotional impact. A strong grasp of UX basics ensures your product is both functional and enjoyable.
Why Understanding User Experience Basics Is Important
Understanding the user experience basics is critical for several reasons:
- Improves User Satisfaction
A product that is easy to use and enjoyable increases user satisfaction. - Boosts Conversions
Websites or apps with good UX often convert more visitors into customers. - Reduces Support Costs
Intuitive interfaces reduce confusion and the need for customer support. - Builds Brand Loyalty
A positive experience encourages users to return and recommend your product. - Enhances Accessibility
Good UX ensures that products are inclusive for users with disabilities or varying abilities.
Core Principles of User Experience Basics
To master UX, it is important to know the foundational principles.
1. Usability
A product should be simple, intuitive, and easy to navigate.
Example: Clear menus, easy-to-find buttons, and logical flow.
2. Accessibility
UX should be inclusive, ensuring everyone, including people with disabilities, can use the product.
Example: Using screen reader-friendly elements, high contrast, and adjustable font sizes.
3. Consistency
Consistency in layout, design, and interaction patterns improves learnability.
Example: Buttons, colors, and typography remain consistent across pages.
4. Feedback
Users need feedback for their actions, such as confirmation messages or error alerts.
Example: “Your payment has been successfully processed.”
5. Efficiency
Tasks should be easy and quick to complete.
Example: Streamlined checkout process in an e-commerce website or auto-fill forms.
6. Emotional Impact
UX is not just functional—it also creates an emotional response.
Example: Friendly illustrations, microanimations, and personalized greetings enhance user satisfaction.
Key Elements in User Experience Basics
To build effective UX, consider these core elements:
- Visual Design – Colors, typography, layout, and aesthetics
- Information Architecture – Organizing content logically and intuitively
- Interaction Design – How users interact with buttons, forms, and menus
- Content – Clear, concise, and valuable information
- Performance – Fast loading times, smooth navigation, and minimal errors
- User Research – Understanding your audience through surveys, interviews, and analytics
User Experience Basics in Web Design
UX is critical in web design. Focusing on user experience basics ensures your website is user-friendly, engaging, and effective.
Tips for Web UX:
- Use intuitive navigation menus
- Ensure responsive design for all devices
- Prioritize mobile-friendly layouts
- Maintain readable fonts, spacing, and hierarchy
- Provide accessible color contrast and clear call-to-action (CTA) buttons
User Experience Basics in Mobile Apps
Mobile apps have unique UX challenges due to smaller screens and touch interactions.
Best Practices:
- Large, tappable buttons
- Clear navigation patterns
- Minimal steps to complete tasks
- Feedback for gestures and interactions
- Offline functionality for usability without internet
User Experience Basics in E-Commerce
UX is particularly important in online shopping.
Key Considerations:
- Simple product navigation and filtering
- Clear pricing and product descriptions
- Streamlined checkout process
- Fast loading pages
- Trust indicators such as reviews, ratings, and security badges
A seamless e-commerce UX improves conversion rates, reduces cart abandonment, and encourages repeat purchases.
User Experience Basics in SaaS Products
Software as a Service (SaaS) products rely heavily on UX for adoption and retention.
Best Practices:
- Onboarding tutorials for new users
- Intuitive dashboards and navigation
- Contextual help and tooltips
- Regular updates based on user feedback
- Clear error messages and troubleshooting support
Good SaaS UX ensures long-term retention and satisfaction.
How to Measure User Experience Basics
Measuring UX helps identify problems and improve your product.
Common Methods:
- Usability Testing – Observe real users interacting with your product
- Surveys & Feedback – Collect insights on satisfaction and pain points
- Analytics – Track engagement, drop-offs, bounce rates, and navigation patterns
- A/B Testing – Compare different designs or flows to see which performs better
- Heatmaps – Identify where users click and scroll
Measurement is crucial for improving UX iteratively.
Common Mistakes in User Experience Basics
Even experienced designers make UX mistakes.
Mistake 1: Ignoring User Needs
Designing for yourself instead of your target audience.
Mistake 2: Overcomplicating Interfaces
Too many options or steps frustrate users.
Mistake 3: Neglecting Mobile UX
Many users access products via mobile devices.
Mistake 4: Poor Accessibility
Failing to consider users with disabilities reduces reach and satisfaction.
Mistake 5: Slow Performance
Loading delays or laggy interactions harm user experience.
Examples of Good User Experience Basics
- Amazon – Easy navigation, fast checkout, personalized recommendations
- Apple – Consistent design and intuitive device interfaces
- Google Search – Simple, fast, and accessible across devices
- Spotify – Personalized playlists, smooth navigation, and visual feedback
These examples show how mastering UX basics leads to success and customer satisfaction.
User Experience Basics in Digital Marketing
UX is also critical in digital marketing. Websites, landing pages, and ads must provide a smooth user journey.
Marketing Tips:
- Clear CTAs in ads and landing pages
- Fast-loading landing pages for campaigns
- Personalized user experiences based on behavior
- Reduce friction in forms and lead generation
Better UX leads to higher conversion rates and ROI.
User Research in User Experience Basics
Understanding your users is fundamental to UX.
User Research Methods:
- Surveys and questionnaires
- Interviews and focus groups
- Heatmaps and session recordings
- Analytics and usage patterns
- Personas and journey maps
Research ensures design decisions meet real user needs.
Future Trends in User Experience Basics
UX is a constantly evolving field.
Emerging Trends:
- Voice User Interfaces (VUI) – Voice commands for navigation
- AI & Personalization – Tailored experiences based on user behavior
- Microinteractions – Small animations or effects for feedback
- Inclusive Design – Greater focus on accessibility and diversity
- Augmented Reality (AR) – Interactive, immersive experiences
- Dark Mode & Customization – User-controlled interface preferences
Keeping up with trends ensures your UX stays modern and competitive.
Conclusion: Mastering User Experience Basics
Mastering user experience basics is essential for anyone involved in digital product design or management. By understanding principles, focusing on usability, accessibility, performance, and emotional impact, and continuously testing and iterating, you can create products that delight users, improve satisfaction, and achieve business goals.
Whether designing a website, mobile app, SaaS platform, or e-commerce store, applying user experience basics ensures